Proper invoice classification is critical for businesses of all sizes. Misclassifying invoices as commercial or non-commercial can lead to compliance issues, financial discrepancies, and operational inefficiencies. Commercial invoices are tied to revenue-generating transactions, while non-commercial invoices are primarily for documentation, internal transfers, or zero-value transactions. Without a clear distinction, businesses risk inaccurate reporting, penalties from tax authorities, and delays in shipping or payments.
Many companies rely on manual processes for creating invoices, which increases the likelihood of human error. Even a small mistake, such as marking a non-commercial shipment as commercial, can have compounding effects on accounting records, audits, and customs documentation. These errors not only impact compliance but can also damage relationships with clients and partners due to disputes or delays.
This guide will provide a comprehensive understanding of the differences between commercial and non-commercial invoices. It will explain common pitfalls that lead to misclassification, outline best practices to prevent errors, and highlight how automation and recurring billing tools, such as ReliaBills, can maintain accurate invoice classification over time.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is a Commercial Invoice?
A commercial invoice is a formal document that records revenue-generating transactions between a seller and a buyer. Its primary function is to provide legal and financial evidence of a sale and support accounting processes, tax filings, and customs clearance for international shipments. Common commercial invoices include sales of goods, professional services, or export transactions that generate income for the business.
Commercial invoices contain key details such as buyer and seller information, itemized product or service descriptions, quantities, unit prices, applicable taxes, shipping costs, and the total amount due. Accuracy in these details ensures the business can report income correctly, collect taxes as required, and resolve potential disputes with customers. A poorly prepared commercial invoice can result in delayed payments, incorrect tax reporting, or audit issues.
For companies operating internationally, commercial invoices are especially critical. Customs authorities rely on these invoices to verify the value of goods, assess duties, and ensure compliance with import/export regulations. Incorrectly prepared commercial invoices may trigger customs delays, fines, or additional documentation requests, further emphasizing the importance of proper classification and preparation.
What Is a Non-Commercial Invoice?
Non-commercial invoices document transactions that do not involve revenue generation but require accurate recordkeeping. Examples include product samples, warranty replacements, internal transfers, donations, or complimentary services. These invoices help businesses track inventory, maintain internal accountability, and satisfy regulatory or customs documentation requirements without recording revenue.
Non-commercial invoices typically include the recipient’s information, description of goods or services, and a clear indication that the transaction is non-commercial. Many businesses mark these invoices as “zero value” or “not for resale” to differentiate them from revenue-generating transactions. Proper labeling ensures that financial records remain accurate and prevents misinterpretation by internal teams, clients, or auditors.
Even though non-commercial invoices do not affect revenue, they still carry compliance responsibilities. International shipments, for example, may require non-commercial invoices for customs purposes. Incorrect classification can lead to disputes with customs authorities, delayed shipments, and operational inefficiencies. Businesses must treat non-commercial invoices with the same attention to detail as commercial invoices to maintain transparency and avoid potential regulatory complications.
Key Differences Between Commercial and Non-Commercial Invoices
Purpose of the Transaction
- Commercial invoices are for revenue-generating sales or services.
- Non-commercial invoices are for documentation, internal transfers, samples, or zero-value items.
- Clear distinction prevents misreporting and ensures proper accounting.
Revenue Recognition and Valuation
- Commercial invoices impact revenue and tax reporting.
- Non-commercial invoices do not affect revenue but maintain record accuracy.
- Accurate classification ensures financial statements reflect true business activity.
Tax and Customs Implications
- Commercial invoices may include taxes, duties, or import/export compliance.
- Non-commercial invoices are often tax-exempt or zero-value but may require customs documentation.
- Correct classification avoids fines, penalties, and shipment delays.
Documentation Requirements
- Commercial invoices require full details: pricing, quantities, customer info, and payment terms.
- Non-commercial invoices need clear labeling, transaction purpose, and traceable records.
Why Misclassification Happens
Invoice misclassification commonly occurs due to inconsistent internal processes, lack of training, or manual errors. Many businesses do not have standardized templates, which can cause employees to incorrectly select an invoice type or reuse templates inappropriately. Even small mistakes, such as using a commercial template for a zero-value shipment, can cause compounding errors.
Human error is another major factor. Manual data entry, copying old invoice templates, or rushing invoice creation without verifying transaction intent often results in misclassification. These mistakes can disrupt accounting, tax reporting, and customs documentation. Over time, repeated errors reduce operational efficiency and increase audit risk.
Misunderstanding the purpose of transactions also contributes to misclassification. Employees may confuse samples or donations with sales transactions, or fail to apply proper labels on invoices. Businesses need clear guidance, verification procedures, and training to reduce these risks and ensure all invoices are classified accurately.
Risks of Misclassifying Invoices
Compliance and Regulatory Issues
- Misclassification can trigger audits, fines, or tax penalties.
- Incorrect reporting of commercial or non-commercial invoices leads to regulatory scrutiny.
- Maintaining accurate records reduces legal and financial exposure.
Customs Delays and Penalties
- For international shipments, misclassified invoices may hold up customs clearance.
- Non-commercial shipments incorrectly marked as commercial may face unnecessary duties.
- Proper labeling ensures smooth logistics and prevents operational disruptions.
Accounting and Reporting Inaccuracies
- Misclassification can distort revenue reporting and affect financial statements.
- This may impact cash flow projections, budgeting, and investor reporting.
- Correct classification safeguards financial accuracy and decision-making.
Customer and Partner Disputes
- Confusing commercial and non-commercial invoices can lead to disputes over payments, deliveries, or services.
- Inaccurate documentation can harm trust and relationships.
- Standardized invoice practices prevent misunderstandings and strengthen business credibility.
How to Correctly Classify Invoices
Correctly classifying invoices starts with understanding the intent of the transaction. Determine if the transaction generates revenue or is meant for internal documentation or compliance purposes. Clear communication with teams about invoice classification criteria is essential to avoid confusion.
Next, verify the value and label invoices accordingly. Zero-value items, samples, and internal transfers should be clearly marked as non-commercial. Include detailed descriptions and metadata to differentiate commercial and non-commercial invoices. Accurate labeling improves internal tracking and audit readiness.
Finally, review applicable tax and shipping regulations. Commercial invoices must comply with tax obligations, while non-commercial invoices may have exemptions. Ensuring compliance before issuance prevents future disputes, fines, and delays. A consistent review process reduces errors and strengthens overall operational efficiency.
Best Practices to Avoid Misclassification
Use Standardized Invoice Templates
- Create separate templates for commercial and non-commercial invoices.
- Include mandatory fields like customer info, description, and transaction type.
- Standardization reduces errors and ensures consistency across the business.
Establish Clear Internal Guidelines
- Define rules for when to use commercial versus non-commercial invoices.
- Train employees on classification protocols and review procedures.
- Clear policies reduce confusion and improve accuracy.
Implement Approval Workflows
- Require supervisor review for exceptions or high-value transactions.
- Verification steps catch potential misclassifications before invoices are sent.
- Workflows reinforce accountability and control.
Regular Invoice Audits and Reviews
- Periodically review issued invoices to identify errors or inconsistencies.
- Use findings to update templates, training, and processes.
- Continuous improvement prevents recurring mistakes and strengthens compliance.
Role of Automation in Invoice Classification
Automation reduces manual decision-making, ensuring invoices are classified consistently. Billing software can automatically apply rules to identify commercial versus non-commercial invoices based on transaction type, customer codes, or internal data fields. This significantly lowers the risk of human error.
Automated systems also maintain audit trails and historical records. Every invoice is tracked and categorized, simplifying compliance reporting, internal audits, and reconciliation. Finance teams spend less time on manual classification, freeing resources for more strategic tasks.
Automation also supports scalability. As a business grows, manual classification becomes increasingly error-prone. Automated workflows maintain consistency across higher transaction volumes, helping businesses avoid misclassification issues while improving operational efficiency.
How Recurring Billing Helps Maintain Consistency
Recurring billing is particularly useful for businesses that issue repeated invoices, such as subscriptions, scheduled deliveries, or warranty replacements. By automating the process, the system ensures the correct invoice type is applied each time, reducing repeated human errors.
Recurring billing also maintains consistent documentation for internal tracking and regulatory compliance. It creates an audit-ready record that aligns with the company’s policies and simplifies reconciliation. This is especially helpful for companies that manage multiple customers or transaction types simultaneously.
Over time, recurring billing prevents compounding errors. Even if human oversight occurs in one cycle, the system automatically applies the correct invoice type in subsequent cycles, ensuring long-term accuracy and reliability.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Treating Non-Commercial Invoices as Exceptions
- All non-commercial transactions should follow formal processes.
- Avoid informal or ad-hoc documentation that increases error risk.
- Consistency ensures traceability and audit readiness.
Changing Invoice Types After Issuance
- Altering invoice classifications post-issuance can create accounting discrepancies.
- Maintain proper labeling and verification before sending.
- Proper upfront classification prevents complications later.
Mixing Manual and Automated Processes
- Combining manual entry with automated systems without controls causes inconsistencies.
- Fully integrated workflows improve accuracy and save time.
- Regular reviews of automation rules maintain alignment with policies.
Failing to Update Templates or Guidelines
- Outdated templates may not reflect new tax rules or business processes.
- Periodically revise templates and classification rules to stay compliant.
- Keep staff informed of changes to prevent errors.
How ReliaBills Helps Prevent Invoice Misclassification
ReliaBills provides a comprehensive solution to prevent invoice misclassification. Its platform allows businesses to create custom templates for both commercial and non-commercial invoices, automatically applying rules based on transaction type. This reduces human error while enforcing consistent standards.
Recurring billing functionality ensures that repeated transactions are accurately classified every cycle. Finance teams can track all invoices centrally, monitor exceptions, and generate detailed reports to maintain compliance. Centralized reporting also simplifies audits and reconciliations, ensuring businesses maintain accurate records effortlessly.
By combining automation, recurring billing, and custom templates, ReliaBills streamlines invoice management. Businesses save time, reduce errors, and improve transparency, allowing finance teams to focus on higher-value tasks and strategic decision-making.
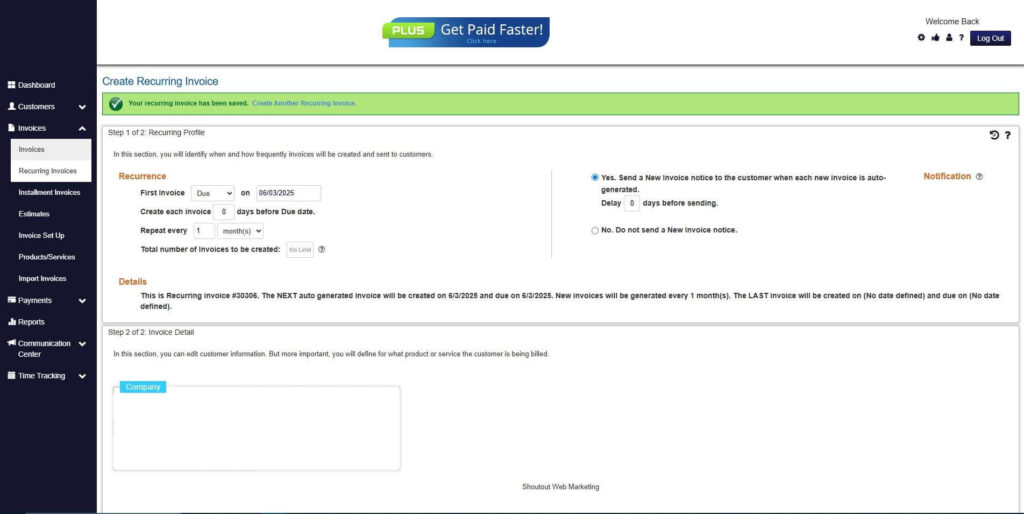
How to Create a New Recurring Invoice Using ReliaBills
Creating a New Recurring Invoice using ReliaBills involves the following steps:
Step 1: Login to ReliaBills
- Access your ReliaBills Account using your login credentials. If you don’t have an account, sign up here.
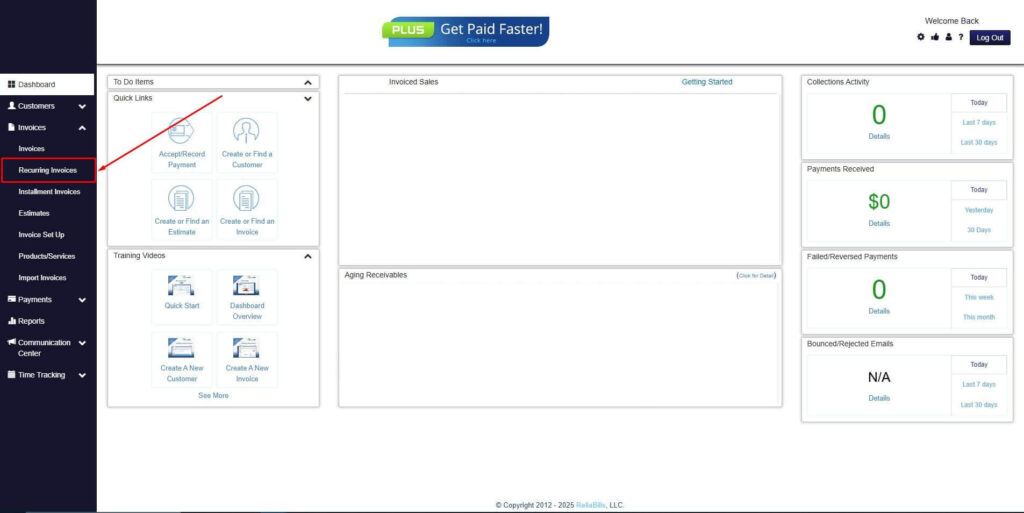
Step 2: Click on Recurring Invoices
- Navigate to the Invoices Dropdown and click on Recurring Invoices for an overview of the list of your existing customers.
Step 3: Go to the Customers Tab
- If you have already created a customer, search for them in the Customers tab and make sure their status is “Active”.
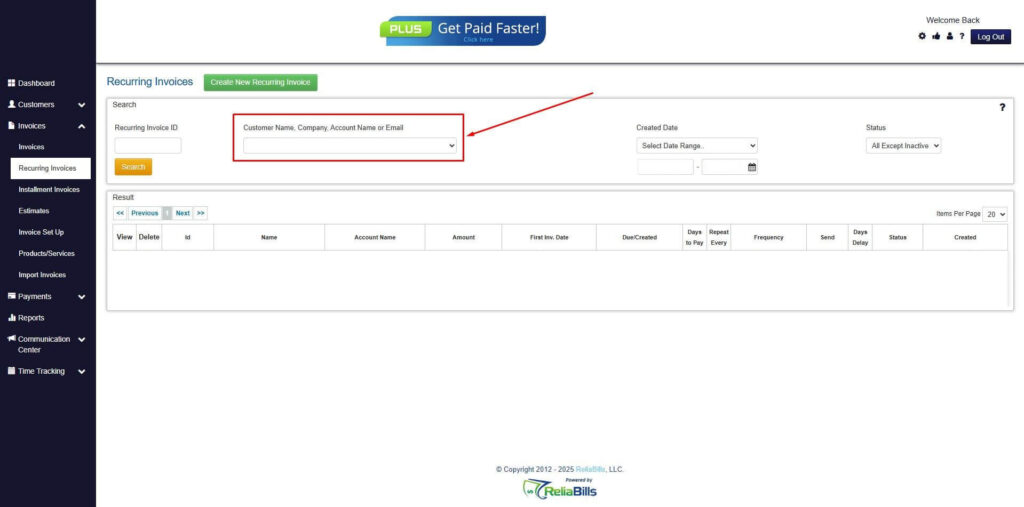
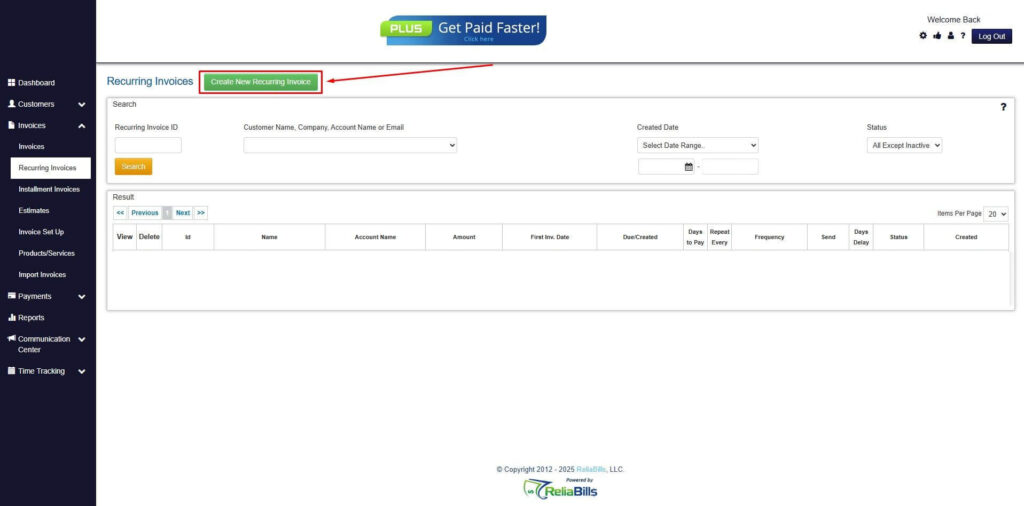
Step 4: Click the Create New Recurring Invoice
- If you haven’t created any customers yet, click the Create New Recurring Invoice to create a new customer.
Step 5: Click on the “Click here” Button
- Click on the “Click here” button to proceed with the recurring invoice creation.
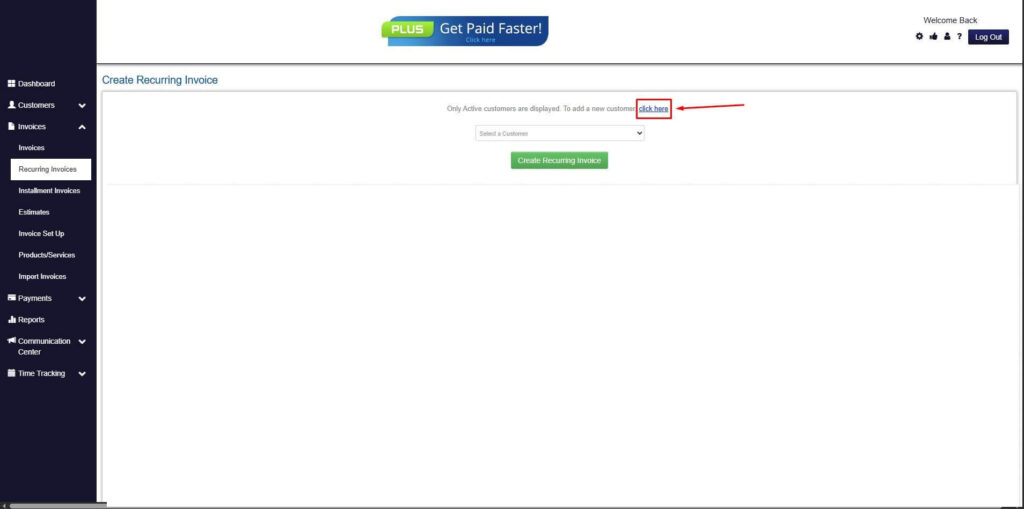
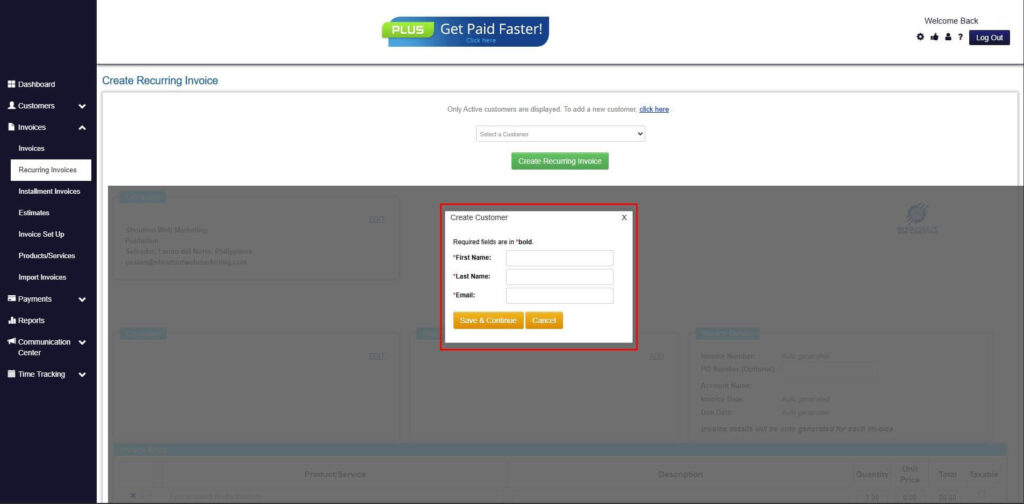
Step 6: Create Customer
- Provide your First Name, Last Name, and Email to proceed.
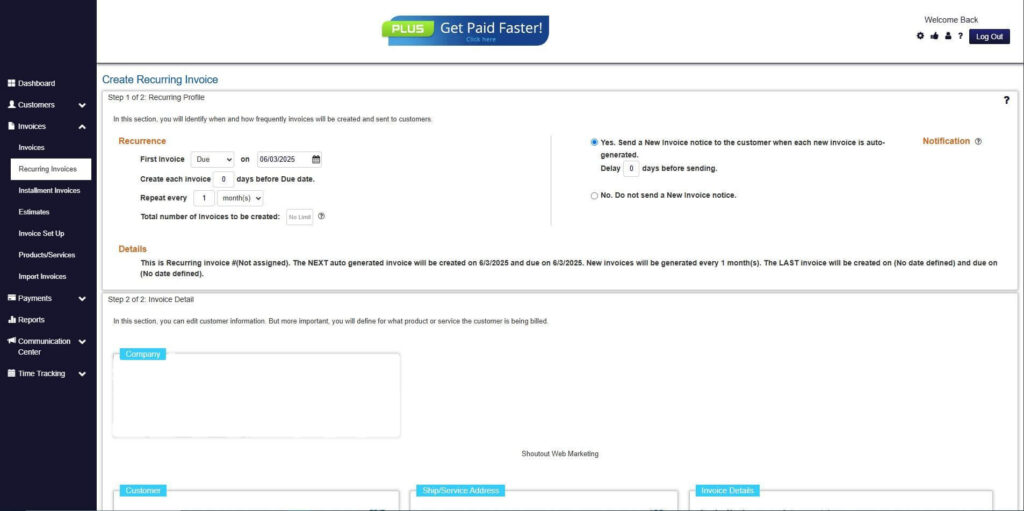
Step 7: Fill in the Create Recurring Invoice Form
- Fill in all the necessary fields.
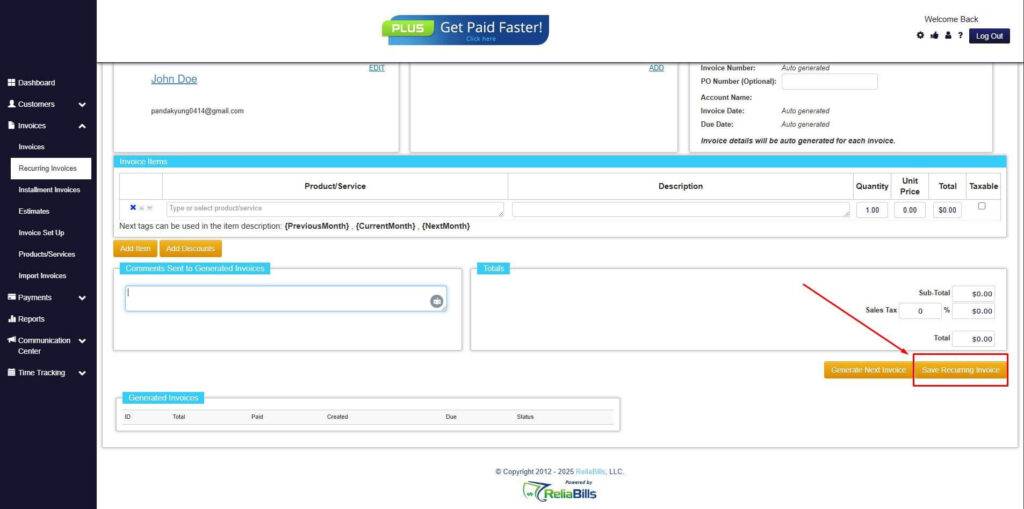
Step 8: Save Recurring Invoice
- After filling up the form, click “Save Recurring Invoice” to continue.
Step 9: Recurring Invoice Created
- Your Recurring Invoice has been created.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can non-commercial invoices include values?
Yes, non-commercial invoices can include values, but they should clearly indicate that the transaction is non-revenue, often marked as zero or “not for resale.” Proper labeling prevents confusion and ensures accurate recordkeeping.
2. Do non-commercial invoices require tax?
Typically, non-commercial invoices are exempt from tax, but international regulations may require documentation for customs or reporting. Businesses should verify local rules before issuing invoices.
3. Can the same customer receive both commercial and non-commercial invoices?
Yes, as long as each invoice is correctly labeled and classified. Proper documentation ensures clients understand the transaction type and avoids disputes.
4. How does automation reduce classification errors?
Automation applies pre-set rules to every invoice, eliminating human error and ensuring consistent classification. Audit trails and recurring billing further enhance accuracy and compliance.
Conclusion
Correctly distinguishing non-commercial vs commercial invoices is essential for operational efficiency, regulatory compliance, and accurate accounting. Implementing standardized templates, internal guidelines, and automation reduces the risk of misclassification and ensures reliable recordkeeping.
Recurring billing strengthens accuracy by applying correct invoice types automatically for repeated transactions, preventing compounding errors. Platforms like ReliaBills offer automation, centralized tracking, and recurring billing features that streamline invoice management, saving time and minimizing human error.
By following these best practices and leveraging technology, businesses can maintain accurate invoices, comply with regulations, and enhance operational efficiency, ensuring smooth financial operations and strong relationships with clients and partners.

