Determining how often to run payroll is a foundational decision for any small business. Payroll frequency affects far more than payday timing. It influences employee satisfaction, administrative workload, legal compliance, and most importantly, cash flow planning. For small business owners, especially those managing payroll for the first time, this decision can feel more complex than expected.
Many small businesses struggle with questions such as how frequently employees should be paid, whether certain payroll schedules are legally required, and how payroll timing impacts taxes and budgeting. These concerns are amplified when revenue is inconsistent or when businesses are managing a mix of hourly and salaried employees.
This guide breaks down everything small business owners need to know about choosing the right payroll schedule. It explains payroll frequencies, legal considerations, employee expectations, and how predictable revenue supports consistent payroll operations.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Does “Running Payroll” Mean?
Running payroll refers to the full process of paying employees accurately and on time for a specific pay period. This process begins with collecting work hours or salary data and ends with employees receiving their pay. Along the way, payroll includes calculating gross wages, withholding taxes, applying deductions, and documenting payments.
Payroll processing is often confused with payroll payment, but the two are different. Payroll processing involves calculations, tax compliance, and recordkeeping, while payroll payment is the act of distributing wages through direct deposit or checks. Both steps must be completed correctly to avoid errors or legal issues.
For small businesses, understanding the scope of payroll helps clarify why payroll frequency matters. Each payroll cycle requires time, attention, and sufficient funds, regardless of business size.
Common Payroll Frequencies Explained
Weekly Payroll
Employees are paid once every week, typically on the same day. This payroll schedule for small business operations is common in industries with hourly workers and fluctuating schedules, such as construction, retail, and hospitality. While employees appreciate the frequent pay, weekly payroll increases administrative effort, processing costs, and the need for consistent cash availability.
Biweekly Payroll
Biweekly payroll runs once every two weeks, resulting in 26 pay periods per year. This is one of the most widely used payroll schedules for small businesses because it balances administrative efficiency with employee expectations. It simplifies overtime calculations since pay periods align with standard workweeks, making it ideal for businesses with both hourly and salaried staff.
Semi-Monthly Payroll
Semi-monthly payroll pays employees twice per month on fixed dates, such as the 15th and last day of the month. This schedule provides predictable paydays, which can help with budgeting for both employees and employers. However, it can complicate overtime calculations for hourly workers, as pay periods do not always match weekly work schedules.
Monthly Payroll
Monthly payroll pays employees once per month and requires the least administrative effort. This option is typically used for salaried employees or executive roles and may not be allowed for hourly workers in certain states. While it simplifies payroll processing, it can create financial strain for employees who rely on more frequent income.
Legal and Compliance Considerations
Payroll schedules are regulated by labor laws, and small businesses must comply with both federal and state requirements. While federal law does not mandate a specific pay frequency, many states impose minimum pay frequency rules, especially for hourly employees.
Some states require weekly or biweekly payroll, while others allow semi-monthly or monthly pay under certain conditions. Businesses operating across state lines must comply with the most restrictive applicable laws.
Overtime regulations also influence payroll scheduling. Payroll schedules that align closely with workweeks make overtime calculations easier and reduce the risk of underpayment. Failure to follow pay frequency laws can result in penalties, back pay claims, and legal disputes.
How Payroll Frequency Affects Employees
Payroll frequency plays a major role in employee financial stability. Employees who are paid more frequently often find it easier to manage household expenses, pay bills on time, and avoid short-term debt.
For hourly workers, longer gaps between paychecks can create financial stress, even if total compensation remains the same. This stress can affect morale, productivity, and retention. Salaried employees may be more flexible, but predictability still matters.
Choosing a payroll schedule that aligns with employee needs demonstrates consideration and professionalism, which can strengthen workplace trust and satisfaction.
How Payroll Frequency Affects Small Business Cash Flow
Payroll is typically one of the largest and most predictable expenses for a small business. The chosen payroll schedule determines when cash must be available to cover wages, taxes, and employer contributions.
More frequent payroll cycles require steady cash inflows and tighter cash management. Less frequent payroll cycles allow more time to accumulate funds but can result in larger cash outflows at once.
Businesses with inconsistent revenue often struggle to maintain timely payroll payments. Aligning payroll schedules with revenue patterns helps prevent cash shortages and last-minute financial strain.
Choosing the Right Payroll Schedule for Your Business
Selecting the right payroll schedule for a small business involves balancing compliance, employee needs, and operational capacity. Business size, industry norms, and workforce composition all play a role.
Hourly-heavy businesses often benefit from weekly or biweekly payroll, while salaried teams may function well on semi-monthly schedules. Administrative capacity also matters, as frequent payroll runs require more time and oversight.
Evaluating payroll costs, available resources, and employee expectations helps business owners choose a payroll schedule that is sustainable and scalable.
Payroll Frequency for Different Business Types
Service-Based Businesses
Consulting firms, agencies, and professional service providers often choose biweekly or semi-monthly payroll. These schedules align well with client billing cycles and recurring revenue models, making it easier to manage payroll cash flow.
Retail and Hospitality Businesses
Businesses in retail, food service, and hospitality frequently use weekly or biweekly payroll. These industries rely heavily on hourly workers with variable schedules, and more frequent payroll helps employees manage income fluctuations while simplifying overtime compliance.
Contractors and Project-Based Teams
Companies working with contractors or project-based employees may structure payroll around project milestones or completion dates. While flexibility is important, businesses must still ensure compliance with worker classification and payment timing laws.
Remote and Multi-State Teams
Businesses with remote employees or staff in multiple states must consider state-specific pay frequency laws. Payroll schedules often need to accommodate the most restrictive state requirements to remain compliant across all locations.
Managing Payroll More Efficiently
As a business grows, payroll becomes more complex. Manual payroll processes increase the risk of errors, missed deadlines, and compliance issues. Automating payroll calculations reduces manual effort and improves accuracy.
Payroll software and outsourced payroll services help ensure taxes are calculated correctly, payments are made on time, and filings are completed accurately. Automation also creates consistent payroll processes that scale with business growth.
Efficient payroll management saves time and allows business owners to focus on revenue-generating activities.
How Predictable Revenue Supports Payroll Scheduling
A stable payroll schedule depends on reliable cash inflows. Businesses with unpredictable revenue often struggle to plan payroll expenses and maintain sufficient reserves.
Predictable revenue makes it easier to budget for payroll, schedule payments confidently, and avoid payroll delays. Automated invoicing and recurring billing help create consistent income streams that support payroll obligations.
When revenue timing aligns with payroll cycles, businesses experience fewer cash flow disruptions and greater financial stability.
Common Payroll Frequency Mistakes to Avoid
Choosing Payroll Frequency Based Only on Convenience
Selecting a payroll schedule that is easy for the employer but misaligned with cash flow or employee needs can lead to financial strain and dissatisfaction.
Ignoring State and Local Pay Frequency Laws
Each state may impose minimum pay frequency rules, especially for hourly employees. Overlooking these regulations can result in penalties, back pay obligations, and compliance issues.
Changing Payroll Schedules Too Often
Frequent changes to payroll timing can confuse employees, disrupt budgeting, and increase administrative errors. Payroll schedules should be stable and well-communicated.
Failing to Align Payroll with Revenue Timing
Running payroll without considering when revenue is collected can cause cash shortages. Businesses should align payroll schedules with predictable income streams whenever possible.
How ReliaBills Supports Reliable Payroll Scheduling
ReliaBills helps small businesses maintain a reliable payroll schedule by strengthening the underlying cash flow processes that support regular pay runs. With automated invoicing, businesses can ensure bills are generated and sent on time without manual effort. This reduces delays in payment collection and improves overall cash flow visibility, enabling business owners to forecast incoming revenue more confidently and align it with upcoming payroll obligations.
Recurring billing is a key feature that contributes to payroll readiness. ReliaBills allows you to set up automated invoicing for ongoing services or retainer arrangements, creating a predictable inflow of funds. By reducing the need for manual invoicing and follow-ups, recurring billing helps stabilize revenue streams, which in turn supports consistent payroll funding and reduces the risk of cash shortages at critical payroll dates.
In addition, ReliaBills centralizes payment tracking and reporting, giving small business owners a clear view of accounts receivable. Detailed reports on outstanding invoices, payment status, and historical billing activity make it easier to plan and prioritize financial obligations. This real-time insight allows business owners to make informed decisions about timing payroll runs, ensuring employees are paid on schedule while maintaining healthy operational cash flow.
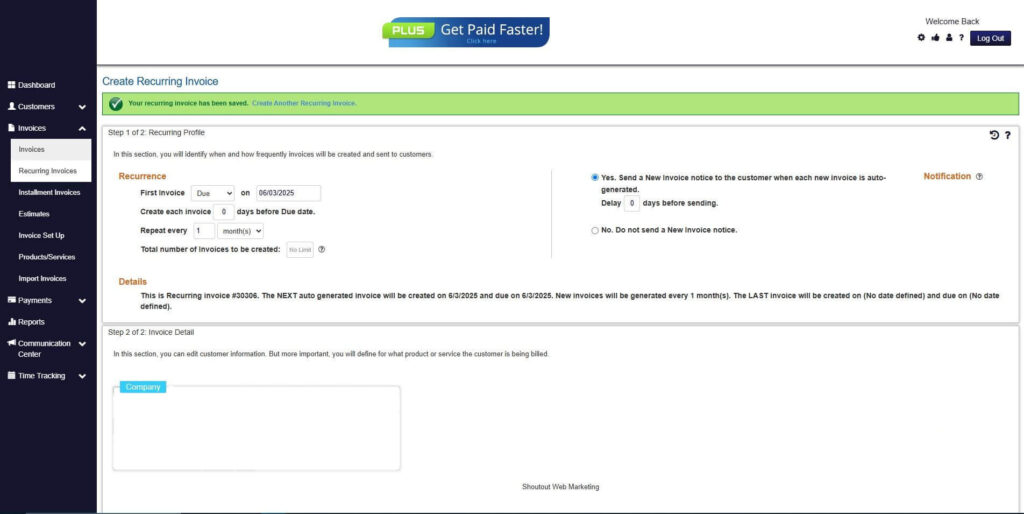
How to Create a New Recurring Invoice Using ReliaBills
Creating a New Recurring Invoice using ReliaBills involves the following steps:
Step 1: Login to ReliaBills
- Access your ReliaBills Account using your login credentials. If you don’t have an account, sign up here.
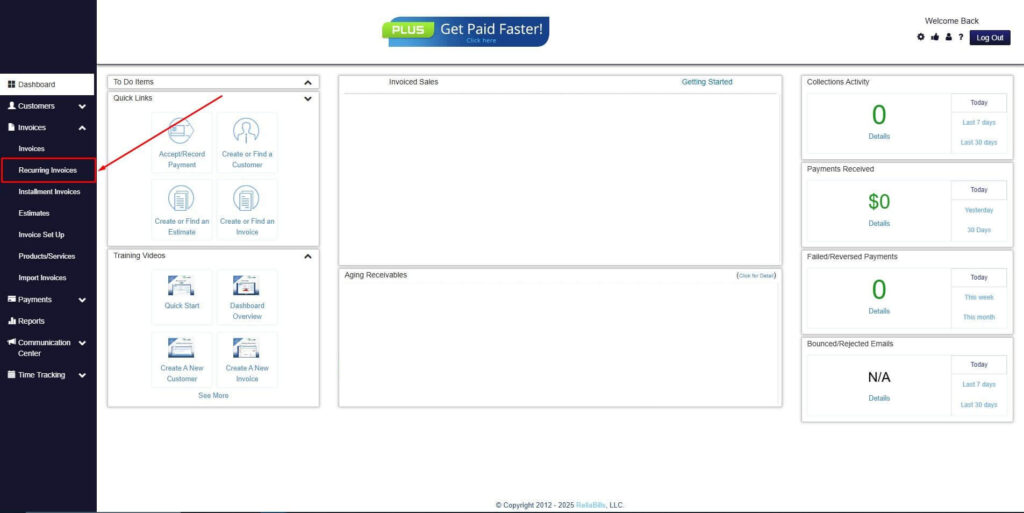
Step 2: Click on Recurring Invoices
- Navigate to the Invoices Dropdown and click on Recurring Invoices for an overview of the list of your existing customers.
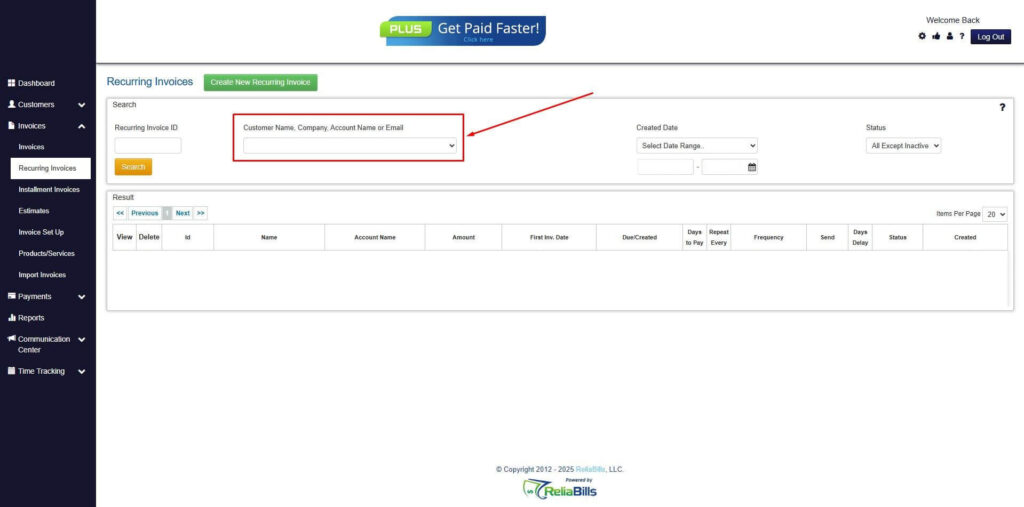
Step 3: Go to the Customers Tab
- If you have already created a customer, search for them in the Customers tab and make sure their status is “Active”.
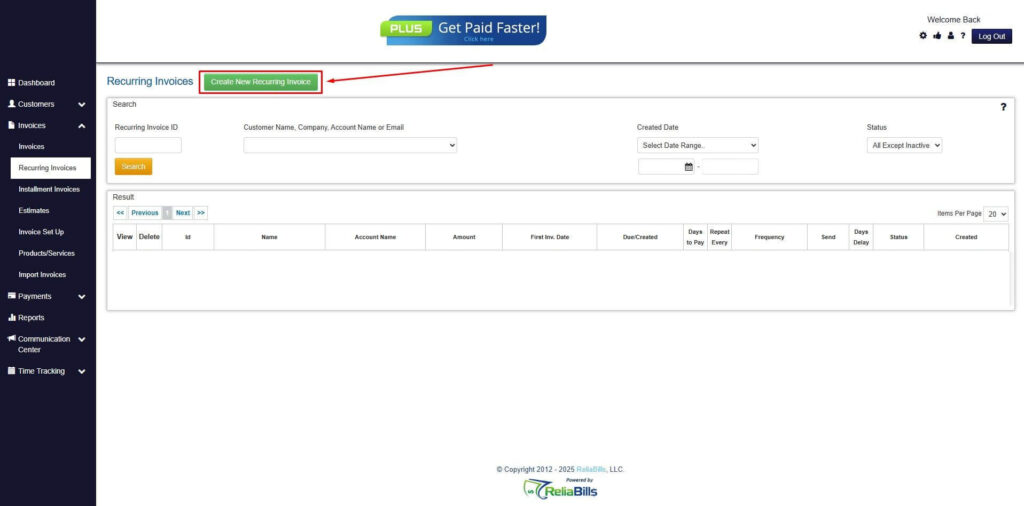
Step 4: Click the Create New Recurring Invoice
- If you haven’t created any customers yet, click the Create New Recurring Invoice to create a new customer.
Step 5: Click on the “Click here” Button
- Click on the “Click here” button to proceed with the recurring invoice creation.
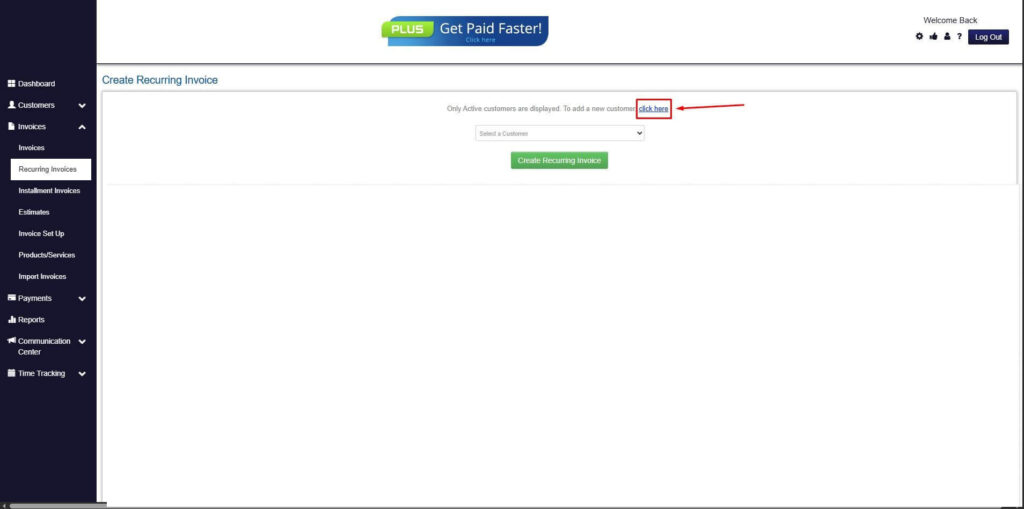
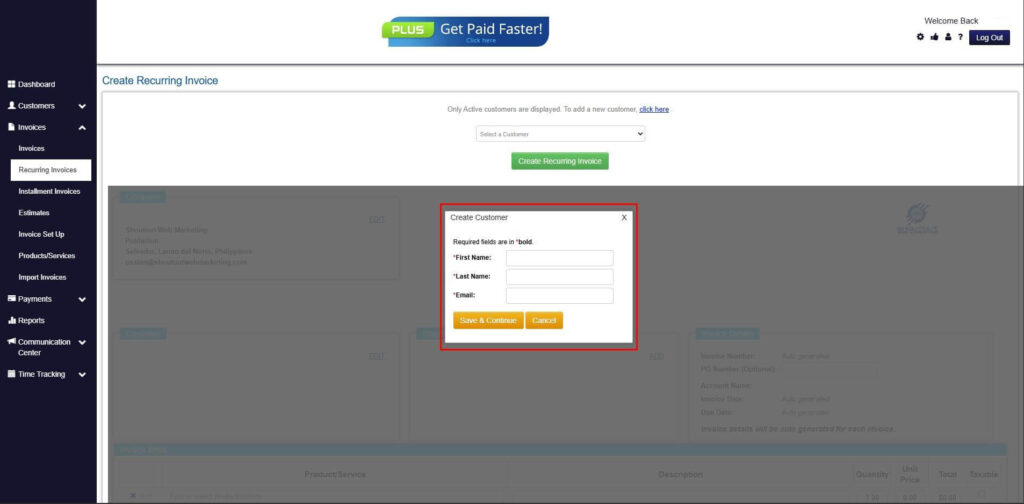
Step 6: Create Customer
- Provide your First Name, Last Name, and Email to proceed.
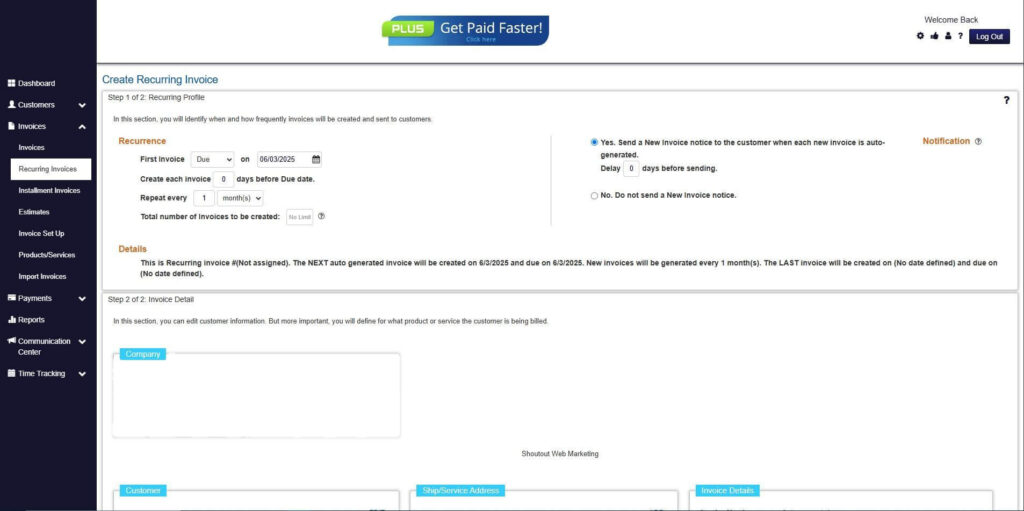
Step 7: Fill in the Create Recurring Invoice Form
- Fill in all the necessary fields.
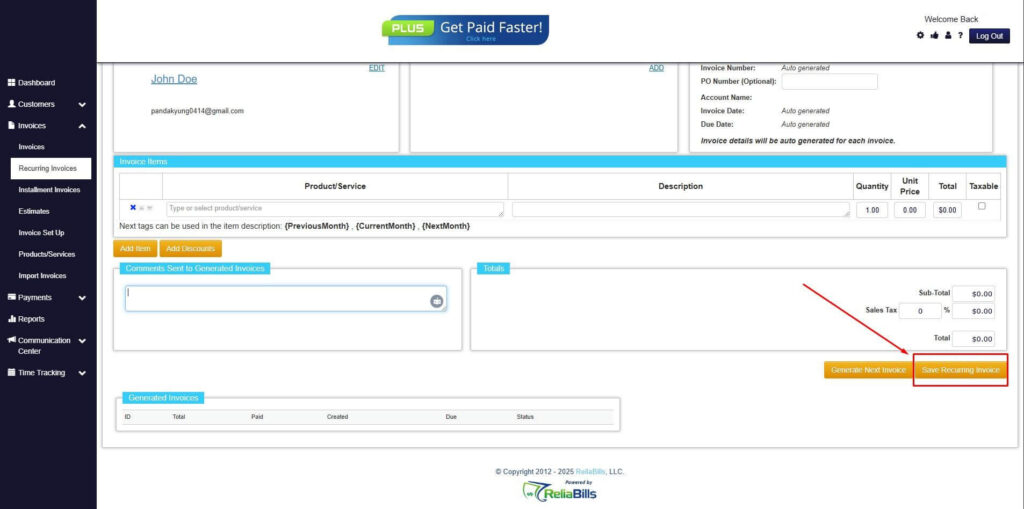
Step 8: Save Recurring Invoice
- After filling up the form, click “Save Recurring Invoice” to continue.
Step 9: Recurring Invoice Created
- Your Recurring Invoice has been created.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can payroll frequency be changed?
Yes, payroll frequency can be changed, but businesses must comply with applicable state laws and provide advance notice to employees before making any changes.
2. Is biweekly or semi-monthly payroll better for small businesses?
Biweekly payroll often works better for businesses with hourly employees due to easier overtime calculations, while semi-monthly payroll may suit salaried teams that prefer fixed pay dates.
3. What payroll schedule is best for startups?
Many startups choose biweekly payroll because it balances administrative workload, employee expectations, and cash flow management during early growth stages.
4. Does payroll frequency affect payroll taxes?
Payroll frequency does not change tax rates, but it does affect when taxes are withheld, reported, and paid. More frequent payroll cycles require more frequent tax calculations and filings.
Conclusion
Choosing the right payroll schedule for small business operations requires careful consideration of legal requirements, employee needs, and cash flow realities. Payroll frequency impacts financial stability, compliance, and overall business efficiency.
By aligning payroll schedules with predictable revenue and using tools that support consistent cash inflows, small businesses can reduce risk and improve payroll reliability. With automated invoicing and recurring billing, platforms like ReliaBills help businesses maintain dependable payroll schedules and support long-term growth.

