Payroll is one of the most critical responsibilities for any new employer, yet it is also one of the most error-prone. Many beginners underestimate the complexity of payroll, assuming it is simply about paying employees on time. In reality, payroll involves tax compliance, accurate calculations, recordkeeping, and strict deadlines that leave little room for error.
Payroll mistakes can create serious financial and legal consequences for small businesses. Errors may lead to penalties, employee dissatisfaction, or audits that disrupt daily operations. Even small miscalculations can compound over time and affect cash flow and trust.
This guide breaks down the most common payroll mistakes beginners make and explains how to avoid them. By understanding these risks early, new employers can build stronger payroll processes and protect their business from costly setbacks.
Table of Contents
ToggleCommon Payroll Mistakes Beginners Make
1. Misclassifying Employees and Contractors
One of the most common payroll mistakes to avoid is misclassifying workers as independent contractors instead of employees. Employees and contractors are treated very differently for payroll and tax purposes, and using the wrong classification can trigger serious compliance issues. Beginners often misclassify workers to simplify payroll or reduce tax obligations.
Misclassification affects payroll taxes, benefits, and legal protections. Employees require income tax withholding, Social Security, Medicare, and often benefits, while contractors do not. Treating an employee as a contractor can result in unpaid taxes, penalties, and back wages.
Beginners frequently make classification errors when hiring remote workers or short-term help. Without understanding federal and state guidelines, businesses may unintentionally violate labor laws, making this one of the most important payroll mistakes to avoid early on.
2. Incorrect Payroll Tax Withholding
Incorrect tax withholding is another frequent payroll issue for beginners. Federal income tax calculations depend on accurate employee forms, such as W-4s, and even small errors can result in underpayment or overpayment. Both situations create administrative headaches and potential penalties.
Mistakes with Social Security and Medicare taxes are also common. These taxes have fixed rates, but beginners sometimes apply outdated percentages or fail to account for wage limits. Errors in these calculations directly affect both employee pay and employer tax obligations.
State and local tax withholding adds another layer of complexity. Tax rates and rules vary widely by location, and beginners often overlook local requirements. Missing these details can quickly place a business out of compliance.
3. Missing Payroll Tax Deadlines
Payroll tax deadlines are strict, and missing them is one of the costliest payroll mistakes to avoid. New employers may not realize how frequently payroll taxes must be deposited or how many filings are required throughout the year. Late payments often result in penalties and interest that add up quickly.
Beginners commonly miss deadlines for federal deposits, quarterly filings, or annual forms. These reporting obligations are separate from employee pay schedules, which can cause confusion. Without a clear calendar, it is easy to fall behind.
Missing deadlines can also raise red flags with tax authorities. Repeated late filings increase the likelihood of audits and enforcement actions, creating long-term compliance risks for the business.
4. Errors in Calculating Gross Pay
Calculating gross pay accurately is essential, yet beginners frequently make mistakes in this area. Errors often occur when calculating hourly wages, especially when employees work variable schedules. Incorrect pay rates or missed hours directly affect employee trust.
Overtime calculations are another common problem. Overtime rules vary by jurisdiction, and beginners may apply the wrong multiplier or fail to recognize when overtime applies. Bonuses and commissions can also be miscalculated if not clearly defined.
Inaccurate time tracking contributes heavily to gross pay errors. Manual timekeeping systems increase the risk of missed entries or incorrect totals, making this one of the most avoidable payroll mistakes to avoid with better processes.
5. Overlooking Employer Payroll Taxes
Many beginners focus only on employee deductions and forget about employer payroll taxes. Employers are responsible for their share of Social Security and Medicare taxes, which must be calculated and paid separately. Overlooking these obligations can create unexpected liabilities.
Unemployment taxes are another area often missed. Federal and state unemployment taxes apply even if the business has only a few employees. Beginners may fail to register or file these taxes correctly.
Other mandatory contributions, such as workers’ compensation premiums, may also be overlooked. These costs must be included in payroll planning to avoid surprises that strain cash flow.
6. Poor Payroll Recordkeeping
Accurate payroll recordkeeping is a legal requirement, yet many beginners fail to maintain complete records. Missing payroll reports, time logs, or tax filings can make it difficult to resolve disputes or respond to audits. Poor documentation increases compliance risks.
Retention requirements vary by jurisdiction, and beginners may not know how long payroll records must be kept. Discarding records too early can create serious problems during inspections or employee claims.
Strong recordkeeping supports transparency and accountability. Without it, businesses struggle to track payroll history, correct errors, or demonstrate compliance when required.
7. Not Staying Updated on Payroll Laws
Payroll laws change regularly, and beginners often fall behind on updates. Changes in tax rates, minimum wage laws, and filing requirements can impact payroll calculations immediately. Using outdated information is a common payroll mistake to avoid.
State and local regulations add additional complexity, especially for businesses with remote or multi-state employees. Each location may have different rules regarding taxes, benefits, and reporting.
Failing to stay informed can result in unintentional violations. Regular reviews of payroll regulations are essential for maintaining compliance as the business grows.
8. Manual Payroll Processing Errors
Manual payroll processing increases the risk of errors for beginners. Spreadsheets are prone to formula mistakes, incorrect data entry, and version control issues. These small errors can lead to incorrect payments.
Duplicate or missed payments often occur when payroll lacks a clear review process. Without approvals or checks, mistakes may go unnoticed until employees raise concerns.
Manual processes also lack consistency and scalability. As payroll volume increases, manual systems become harder to manage, increasing the likelihood of errors.
9. Payroll Cash Flow Mismanagement
Payroll requires consistent cash availability, but beginners often underestimate total payroll costs. Taxes, benefits, and employer contributions add significantly to base wages, affecting cash flow planning.
Without proper budgeting, businesses may struggle to cover payroll during slow revenue periods. This can delay payments and damage employee trust.
Inconsistent revenue makes payroll even more challenging. Businesses without predictable income are more likely to experience payroll stress, highlighting the importance of financial planning.
How Automation Helps Prevent Payroll Mistakes
Reduces manual calculations
Automation eliminates human error in calculating gross pay, deductions, and taxes. Payroll software consistently applies current tax rates and correctly calculates overtime, bonuses, and benefits, reducing common errors beginners make.
Automates tax filings and payments
Many payroll mistakes come from missed deadlines or incorrect filings. Automated payroll systems handle federal, state, and local tax payments, ensuring taxes are deposited on time and forms are filed correctly.
Improves consistency across payroll cycles
Automation enforces standardized workflows for every pay period. This prevents inconsistent deductions, misapplied benefits, or miscalculated wages, giving employees accurate paychecks every time.
Supports recurring payroll and income management
Integration with recurring billing systems ensures predictable revenue aligns with payroll cycles. Businesses can confidently schedule payroll without fearing cash shortfalls.
Maintains audit-ready records
Automated systems track every calculation and transaction, creating a reliable audit trail. This reduces compliance risks and simplifies payroll reporting.
Best Practices for Beginners
Establish clear payroll processes and schedules
Document step-by-step procedures for collecting timesheets, calculating pay, applying deductions, and processing payments. Consistency reduces errors and improves compliance.
Leverage payroll software or outsourcing
Software solutions and professional payroll services minimize manual mistakes and ensure compliance with tax laws, freeing beginners to focus on running the business.
Review payroll regularly
Periodically check calculations, tax filings, and deductions to catch errors early. Regular reconciliation ensures accuracy and builds confidence in payroll operations.
Educate your team on payroll basics
Train staff responsible for payroll on classification, deductions, and filing deadlines. A knowledgeable team prevents avoidable errors.
Align payroll with cash flow planning
Use recurring billing or predictable invoicing to maintain sufficient funds for payroll obligations. Planning ahead ensures timely employee payments.
How ReliaBills Helps Beginners Manage Payroll Cash Flow Effectively
ReliaBills helps businesses create a more reliable foundation for payroll by ensuring revenue comes in consistently and on schedule, which is vital for covering payroll obligations when they arise. With automated invoicing and recurring billing, ReliaBills eliminates many of the manual steps that slow down payment cycles. Instead of creating and sending invoices manually, you can set up invoice schedules once and let the system generate and deliver them automatically, reducing the chance of late or missing invoices that disrupt cash flow planning.
A core cash flow advantage of using ReliaBills is its recurring billing capability. By configuring invoices to recur on a predetermined schedule, businesses can stabilize income streams from ongoing services, subscriptions, or retainer arrangements. This predictability makes it easier to anticipate when funds will arrive, allowing employers to plan payroll expenses with confidence. Regular incoming revenue reduces uncertainty and helps ensure that employee wages and related tax obligations are met reliably each pay period.
ReliaBills also provides centralized tracking and reporting tools that give business owners a clear view into outstanding invoices, payment histories, and receivables. Instead of manually reconciling payments or chasing overdue accounts, you can use real‑time dashboards and reports to monitor expected cash flow and adjust financial plans as needed. This visibility enhances payroll readiness by reducing surprises and giving leaders the financial clarity needed to meet payroll on time, every time.
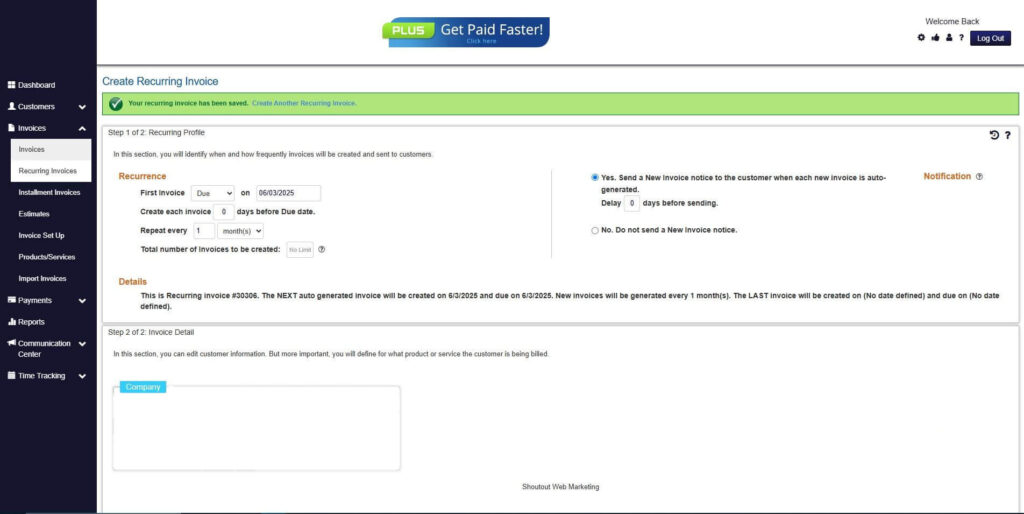
How to Create a New Recurring Invoice Using ReliaBills
Creating a New Recurring Invoice using ReliaBills involves the following steps:
Step 1: Login to ReliaBills
- Access your ReliaBills Account using your login credentials. If you don’t have an account, sign up here.
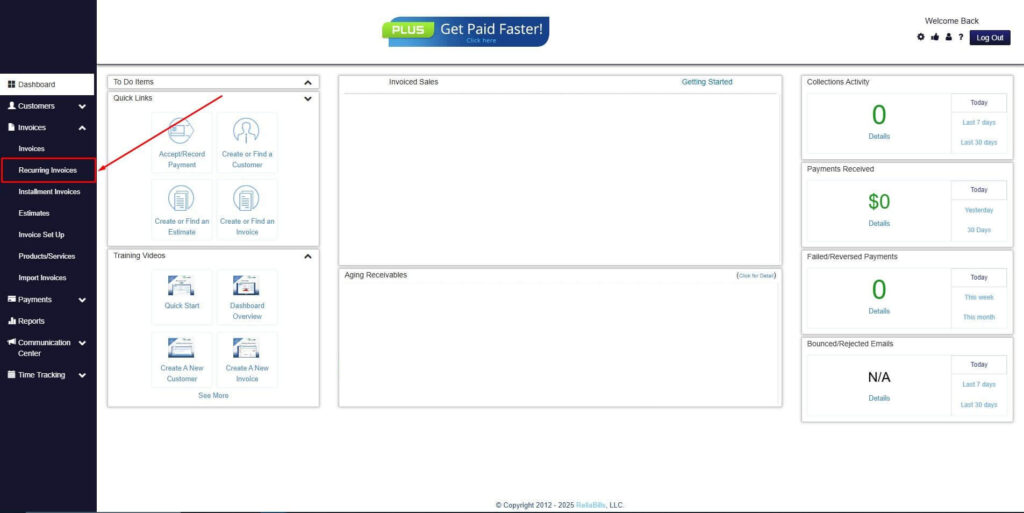
Step 2: Click on Recurring Invoices
- Navigate to the Invoices Dropdown and click on Recurring Invoices for an overview of the list of your existing customers.
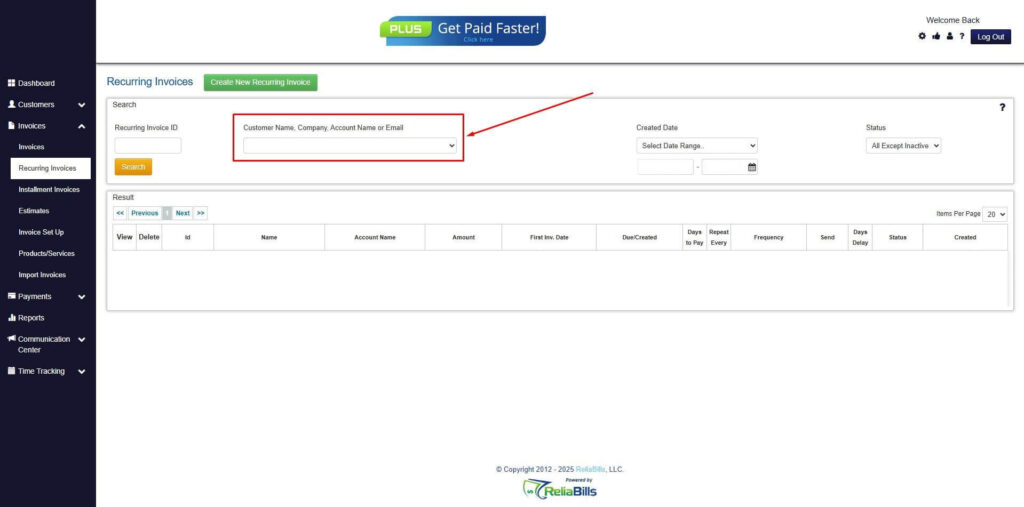
Step 3: Go to the Customers Tab
- If you have already created a customer, search for them in the Customers tab and make sure their status is “Active”.
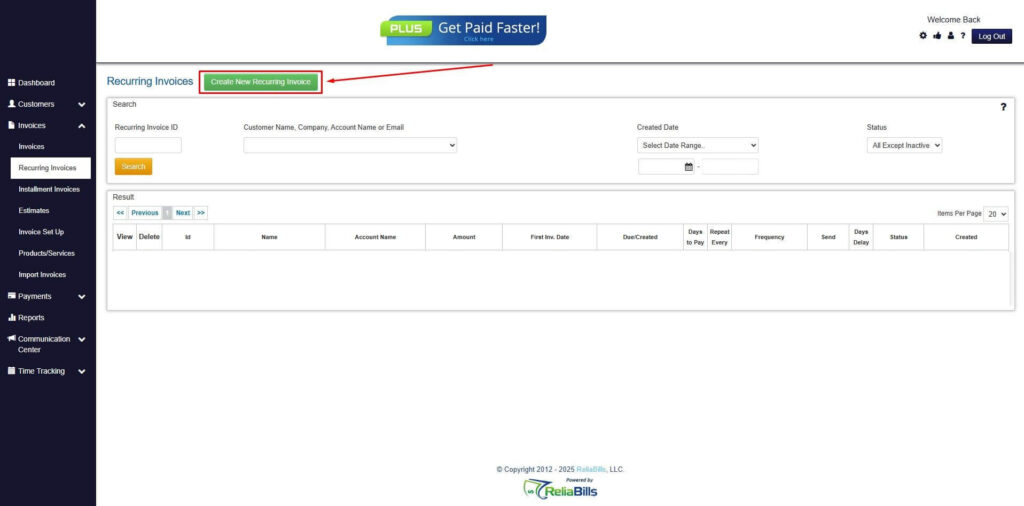
Step 4: Click the Create New Recurring Invoice
- If you haven’t created any customers yet, click the Create New Recurring Invoice to create a new customer.
Step 5: Click on the “Click here” Button
- Click on the “Click here” button to proceed with the recurring invoice creation.
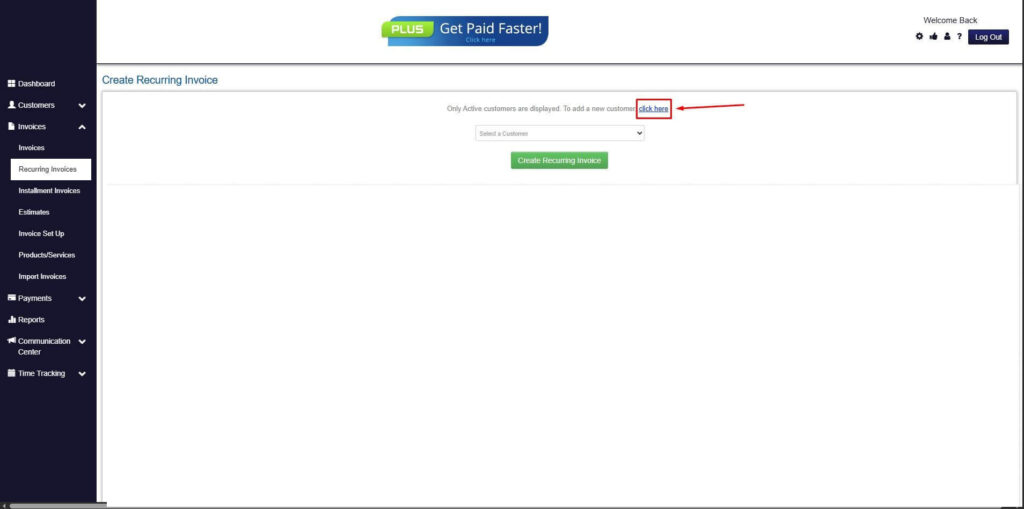
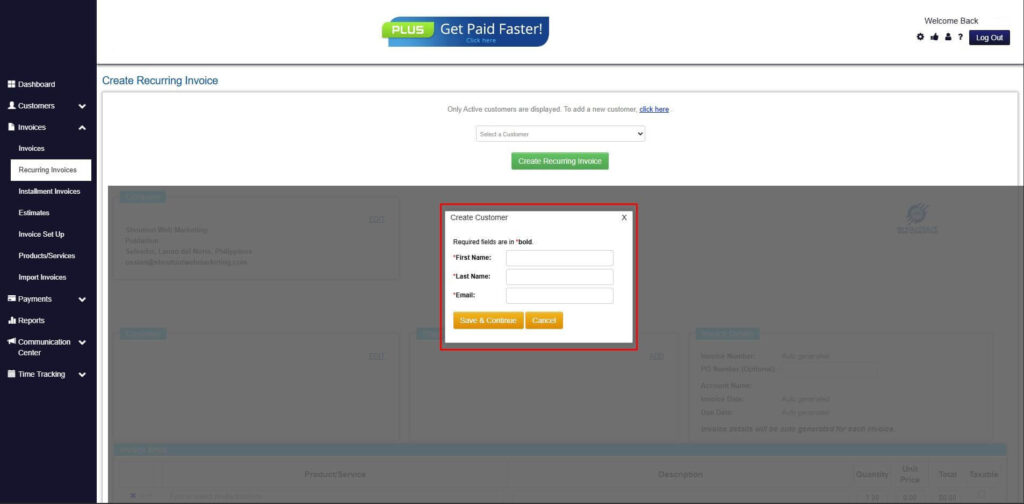
Step 6: Create Customer
- Provide your First Name, Last Name, and Email to proceed.
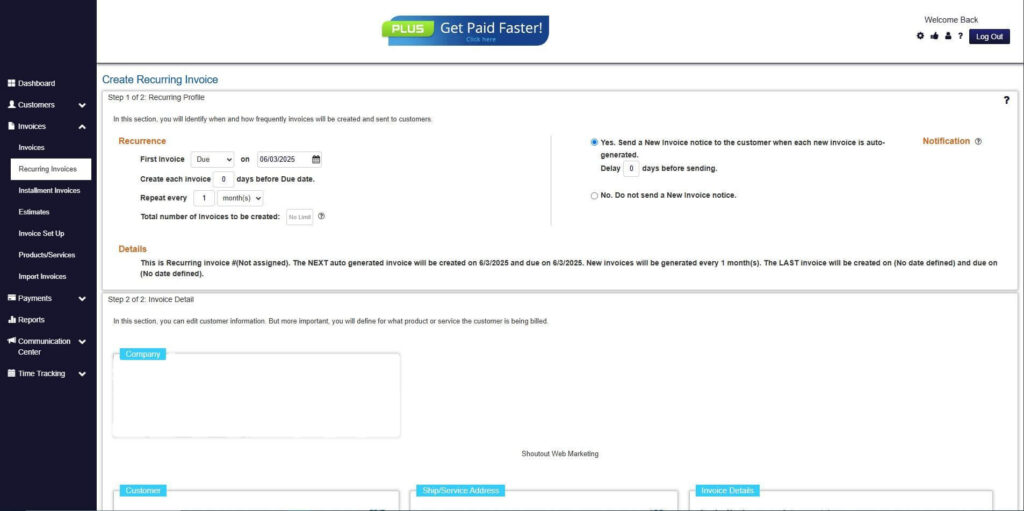
Step 7: Fill in the Create Recurring Invoice Form
- Fill in all the necessary fields.
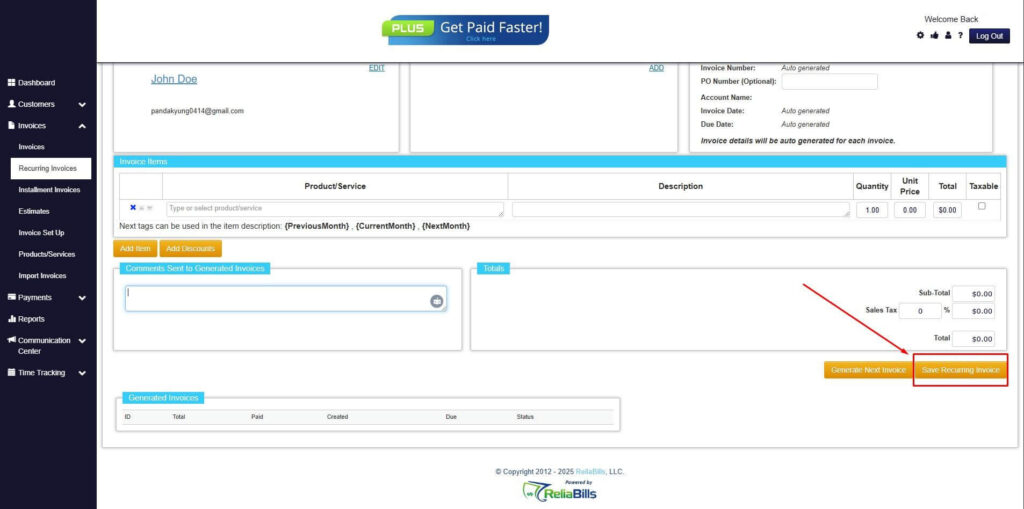
Step 8: Save Recurring Invoice
- After filling up the form, click “Save Recurring Invoice” to continue.
Step 9: Recurring Invoice Created
- Your Recurring Invoice has been created.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How often should payroll be reviewed?
Payroll should be reviewed every pay period to confirm accuracy of gross pay, deductions, and taxes. Regular checks prevent errors from compounding.
2. Can payroll mistakes be corrected?
Yes. Most payroll errors can be corrected through amended filings, adjustments to employee paychecks, or tax corrections, depending on the type of mistake.
3. When should a beginner outsource payroll?
Beginners should consider outsourcing when compliance becomes overwhelming, payroll volume grows, or internal processes are prone to errors. Outsourcing reduces risk and saves time.
4. How does automation reduce payroll errors?
Automation standardizes calculations, applies current tax rules, tracks payments, and provides audit-ready documentation, preventing mistakes that often occur in manual payroll processing.
Conclusion
Payroll mistakes are common among beginners, but most are avoidable with the right knowledge and systems. Misclassification, tax errors, missed deadlines, and poor recordkeeping are among the most frequent payroll mistakes to avoid.
Understanding these risks allows new employers to take proactive steps toward accuracy and compliance. Strong processes and automation reduce errors and improve confidence.
By planning ahead, using the right tools, and maintaining consistent cash flow, beginners can build a reliable payroll foundation that supports long-term business success.

