Compliance plays a critical role in non-commercial invoicing, even when no revenue is exchanged. Transactions such as product samples, warranty replacements, internal transfers, or charitable donations still require accurate documentation and classification. Without proper oversight, small administrative mistakes can escalate into audit concerns or regulatory penalties.
Improper documentation and invoice misclassification create significant exposure. Businesses may accidentally report non-revenue transactions as taxable income or fail to provide required shipping documentation. These issues can distort financial statements and trigger unnecessary scrutiny.
Automation strengthens invoice governance by standardizing processes and reducing manual intervention. With structured workflows and rule-based validation, businesses improve non-commercial invoicing compliance while minimizing costly errors. Accurate records, consistent formatting, and centralized tracking build a stronger foundation for regulatory readiness.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is Non-Commercial Invoicing?
Non-commercial invoicing refers to invoices issued for transactions that do not involve direct sales revenue. These documents are often required for customs, internal accounting, or record-keeping purposes. While they may not represent income, they must still meet compliance standards.
Common use cases include product samples, replacement shipments under warranty, intercompany transfers, donated goods, and internal inventory movements. Even without payment collection, these invoices serve as formal documentation of value and movement.
Unlike commercial invoices, non-commercial invoices should clearly indicate that no revenue is being generated. Proper labeling, classification, and supporting documentation are essential for maintaining non-commercial invoicing compliance and avoiding misreporting.
Key Compliance Risks in Non-Commercial Invoices
Misclassification of Invoice Type
Incorrectly labeling a non-commercial invoice as commercial can result in inaccurate revenue reporting and tax miscalculations. This is one of the most common non-commercial invoicing compliance risks.
Missing Required Documentation
Certain transactions require customs forms, shipment declarations, or internal authorization records. Missing paperwork can delay shipments or trigger audit flags.
Tax and Regulatory Reporting Errors
Even non-revenue transactions may require tax treatment disclosures. Incorrect handling can lead to reporting discrepancies or compliance penalties.
Inconsistent Record-Keeping
Disorganized storage of invoices increases audit risk. Lack of centralized records makes it difficult to retrieve supporting documentation during regulatory reviews.
Regulatory and Audit Considerations
Regulatory standards require consistent documentation, even when transactions are non-commercial. Invoice descriptions must accurately reflect the purpose of goods or services transferred. Clear categorization reduces ambiguity during audits.
Cross-border shipments introduce additional compliance requirements. Customs authorities often require declared value statements, even for samples or donated items. Incomplete documentation can result in delays or fines.
Internal audits also depend on structured invoice management. Businesses must demonstrate that non-revenue transactions are separated from revenue streams. Strong non-commercial invoicing compliance practices protect financial integrity and reporting accuracy.
Why Manual Non-Commercial Invoicing Increases Risk
Manual data entry introduces avoidable human error. Small mistakes in classification, labeling, or tax handling can distort financial records.
Inconsistent formatting creates confusion. Without standardized templates, invoice descriptions and values may vary from one department to another, increasing audit vulnerability.
Lack of centralized tracking makes it difficult to monitor invoice history. Delayed updates or corrections can compound compliance issues, especially when multiple teams handle documentation.
What Is Invoice Automation?
Invoice automation refers to system-driven workflows that generate, categorize, and store invoices based on predefined rules. Instead of relying on manual input, automation enforces consistent standards.
Rule-based validation processes ensure required fields are completed before issuance. This prevents incomplete or incorrectly labeled invoices from being finalized.
Automated data population reduces repetitive entry and strengthens accuracy. Structured storage and digital records improve non-commercial invoicing compliance by making documentation easily retrievable.
How to Reduce Misclassification Through Automation
Use Pre-Defined Invoice Categories
Configure your system with clearly labeled categories such as non-commercial sample, internal transfer, replacement shipment, or donation. Pre-set classifications reduce the risk of staff selecting incorrect invoice types. This directly strengthens non-commercial invoicing compliance by eliminating ambiguity at the point of creation.
Implement Controlled Invoice Templates
Use standardized templates that automatically include required compliance language. Templates can specify “non-revenue transaction” or “no commercial value” where appropriate. Consistent formatting prevents accidental misrepresentation during audits.
Enable Rule-Based Validation Checks
Set up validation rules that flag missing fields, incorrect tax codes, or conflicting classifications. The system should prevent issuance until errors are corrected. This proactive safeguard reduces compliance exposure before documents are finalized.
Restrict Editing Permissions
Limit who can modify invoice classifications or override compliance rules. Role-based access ensures only authorized personnel can adjust sensitive transaction types. Controlled permissions protect reporting accuracy.
Automate Revenue Segmentation
Configure automation to separate revenue and non-revenue transactions within financial reports. This prevents accidental revenue tagging and ensures financial statements remain accurate.
Integrate Approval Workflows
Require secondary review for high-value or cross-border non-commercial invoices. Automated approval chains provide oversight without slowing operational efficiency.
Improving Documentation and Audit Trails
Automated systems create time-stamped invoice records, ensuring transparency. Every modification or issuance is recorded digitally.
Secure digital storage allows businesses to retrieve invoices quickly during audits. Centralized management eliminates scattered spreadsheets and inconsistent recordkeeping.
Comprehensive audit trails strengthen non-commercial invoicing compliance by demonstrating process integrity and accountability.
Strengthening Tax and Regulatory Accuracy
Automation supports proper separation of revenue and non-revenue transactions. Clear categorization prevents incorrect tax application.
When applicable, automated tax handling ensures compliance with jurisdictional rules. This reduces discrepancies in financial reporting.
Accurate documentation lowers regulatory risk and simplifies reporting. Automation ensures that non-commercial transactions are recorded correctly without affecting revenue metrics.
How to Prevent Duplicate or Improper Issuance
Automate Sequential Invoice Numbering
System-generated numbering prevents accidental duplication. Unique identifiers create a clear audit trail and protect record integrity.
Enable Duplicate Detection Controls
Automation can flag invoices with identical reference numbers, customer names, shipment details, or values. Early detection avoids compliance discrepancies.
Use Real-Time Status Tracking
Implement dashboards that show whether an invoice is drafted, approved, issued, or voided. Visibility prevents reissuance of already processed documents.
Require Mandatory Data Fields Before Issuance
Prevent incomplete invoices from being sent. Required fields such as transaction purpose, declared value, and classification ensure documentation accuracy.
Set Automated Alerts for Unusual Activity
If multiple invoices are issued for the same shipment or account within a short timeframe, automated alerts can notify administrators for review.
Maintain Version Control and Revision Logs
Track edits and changes through time-stamped records. This protects non-commercial invoicing compliance by showing transparency during audits.
Integrating Automation with Recurring Billing Systems
Non-commercial invoices must remain separate from recurring revenue workflows. Automation ensures proper categorization without interfering with subscription billing.
Maintaining accurate customer account histories prevents revenue misreporting. Clear segmentation protects financial statements.
Integrated systems provide full visibility across revenue and non-revenue transactions. This alignment enhances both operational efficiency and compliance oversight.
Best Practices for Reducing Compliance Risks
Establish Clear Internal Invoice Policies
Document procedures that define what qualifies as a non-commercial invoice. Clear guidelines reduce confusion across departments.
Standardize Invoice Language Across Teams
Ensure consistent terminology and labeling throughout the organization. Uniform documentation strengthens audit defensibility.
Conduct Periodic Classification Audits
Review invoice categories quarterly to confirm correct segmentation. Proactive audits reduce long-term compliance risk.
Train Employees on Compliance Requirements
Provide structured training on invoice classification, documentation standards, and automation tools. Knowledgeable teams reduce manual mistakes.
Separate Revenue and Non-Revenue Reporting
Maintain distinct financial reporting channels for commercial and non-commercial transactions. This protects financial statement accuracy.
Monitor Key Compliance Metrics
Track metrics such as correction frequency, duplicate issuance rates, and documentation completeness. Monitoring performance helps identify weaknesses early.
Centralize Invoice Storage
Use a secure digital repository for storing and retrieving invoice records. Centralization supports faster audits and better governance.
Leverage Automation Wherever Possible
Manual processes increase variability and risk. Automation ensures consistency, strengthens internal controls, and supports non-commercial invoicing compliance long term.
How ReliaBills Supports Compliance in Non-Commercial Invoicing
ReliaBills provides flexible invoice classification controls that help businesses clearly distinguish between commercial and non-commercial transactions. With customizable templates and structured workflows, companies can standardize documentation and reduce misclassification risks. This structured approach strengthens non-commercial invoicing compliance across departments.
For organizations that manage recurring billing alongside non-revenue transactions, ReliaBills ensures clear separation between recurring revenue workflows and non-commercial invoices. Automated recurring billing operates independently while maintaining centralized visibility, preventing financial misreporting and confusion.
ReliaBills also delivers centralized dashboards, built-in tracking tools, and audit-ready documentation storage. Businesses can monitor invoice activity in real time, retrieve records quickly, and maintain organized compliance documentation. This level of visibility supports governance, reduces administrative burden, and prepares organizations for audits with confidence.
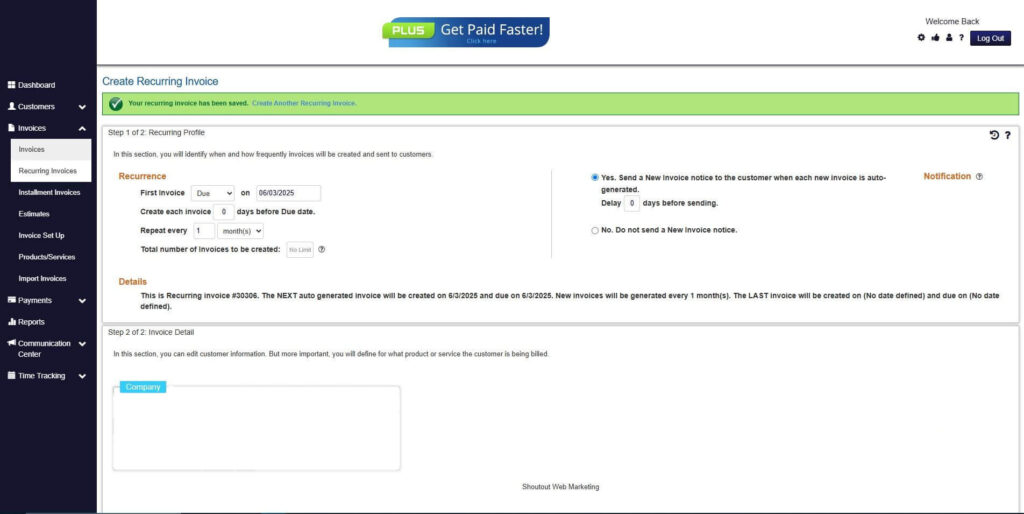
How to Create a New Recurring Invoice Using ReliaBills
Creating a New Recurring Invoice using ReliaBills involves the following steps:
Step 1: Login to ReliaBills
- Access your ReliaBills Account using your login credentials. If you don’t have an account, sign up here.
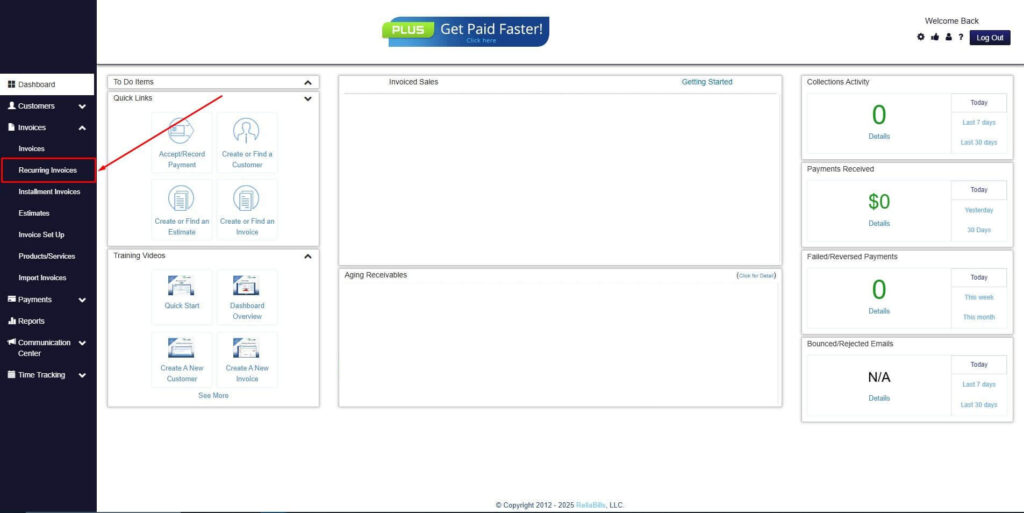
Step 2: Click on Recurring Invoices
- Navigate to the Invoices Dropdown and click on Recurring Invoices for an overview of the list of your existing customers.
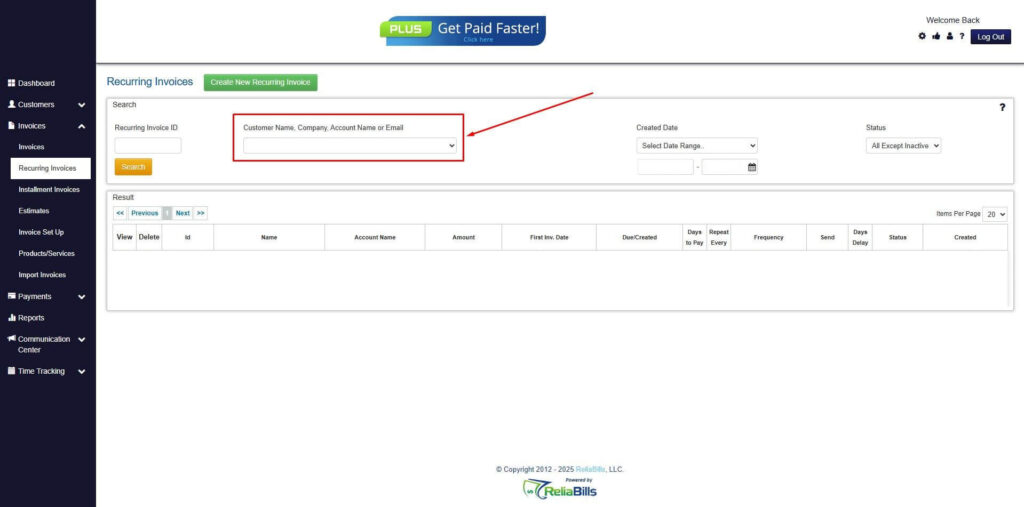
Step 3: Go to the Customers Tab
- If you have already created a customer, search for them in the Customers tab and make sure their status is “Active”.
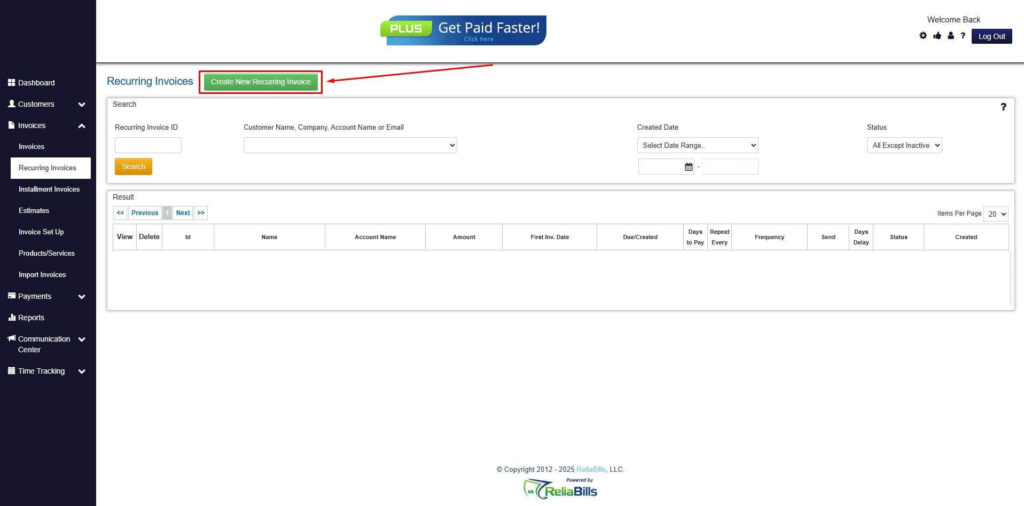
Step 4: Click the Create New Recurring Invoice
- If you haven’t created any customers yet, click the Create New Recurring Invoice to create a new customer.
Step 5: Click on the “Click here” Button
- Click on the “Click here” button to proceed with the recurring invoice creation.
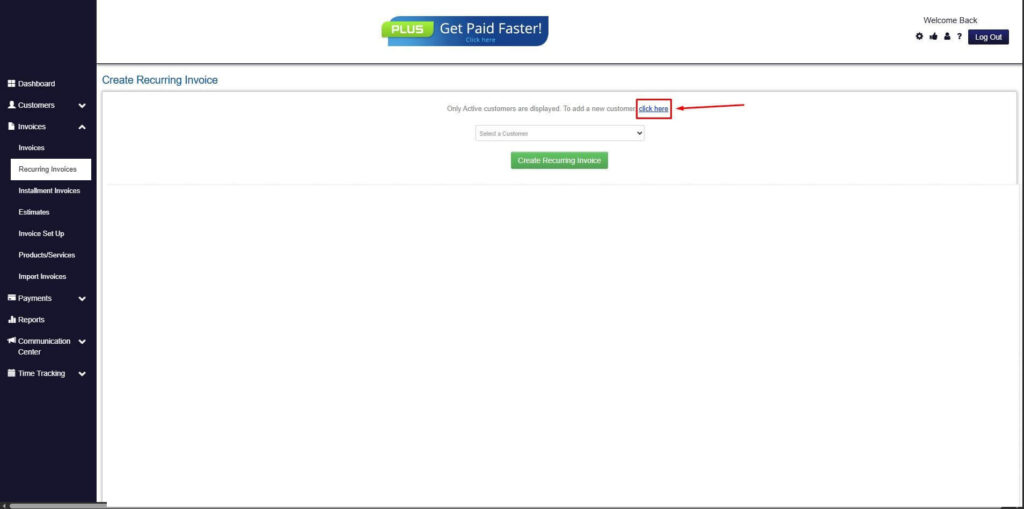
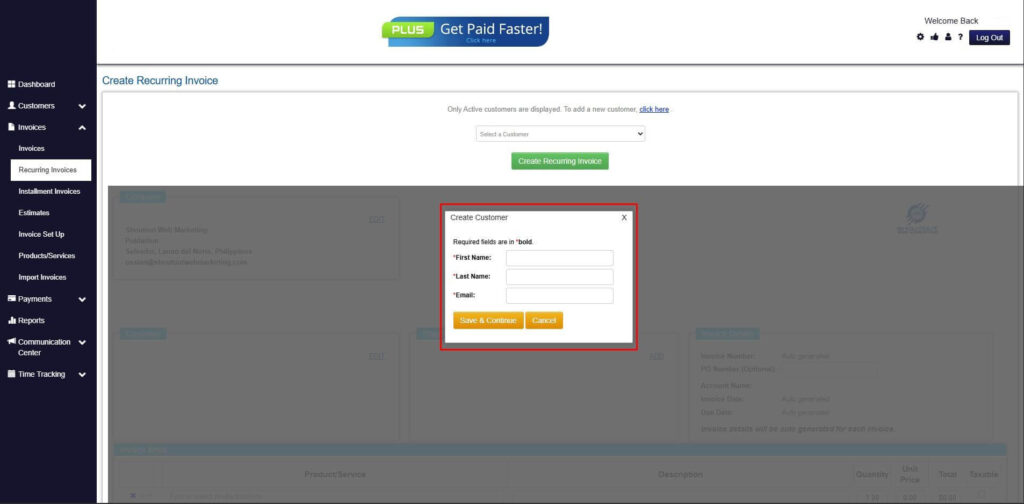
Step 6: Create Customer
- Provide your First Name, Last Name, and Email to proceed.
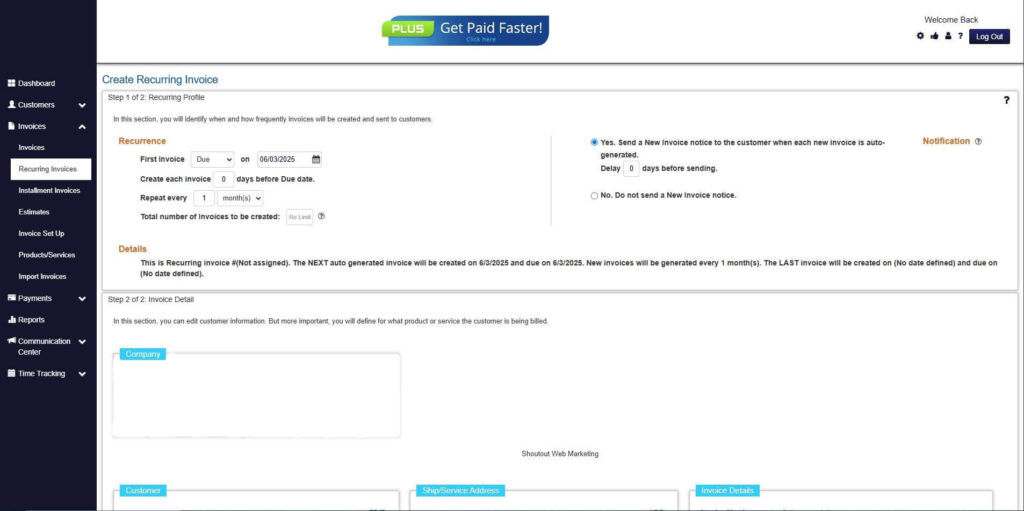
Step 7: Fill in the Create Recurring Invoice Form
- Fill in all the necessary fields.
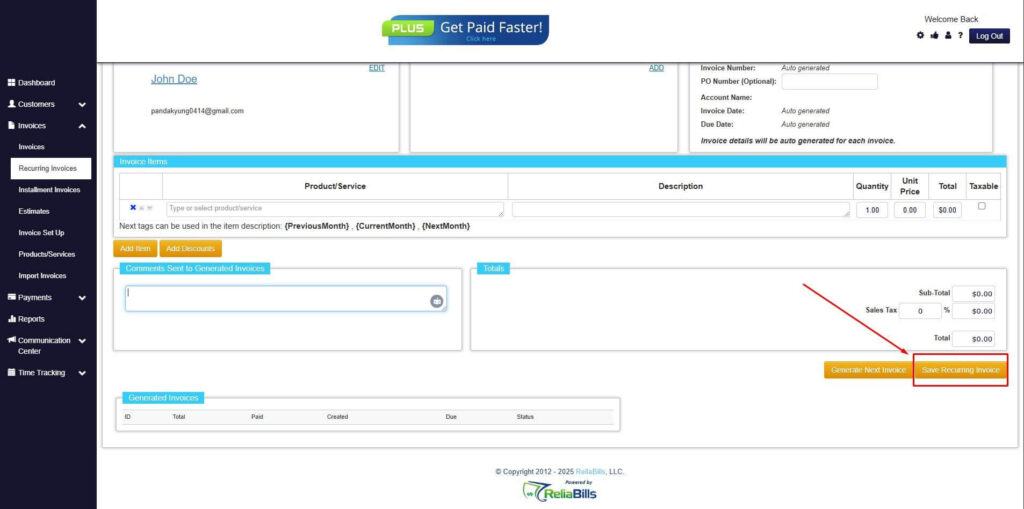
Step 8: Save Recurring Invoice
- After filling up the form, click “Save Recurring Invoice” to continue.
Step 9: Recurring Invoice Created
- Your Recurring Invoice has been created.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What causes misclassification in non-commercial invoicing?
Misclassification typically occurs due to unclear policies, inconsistent templates, or manual data entry errors. Automation reduces these risks through predefined rules and validation checks.
2. Why is duplicate invoice prevention important for compliance?
Duplicate invoices can distort financial records and create confusion during audits. Automated tracking protects data integrity.
3. Can non-commercial invoices affect tax reporting?
Yes. Even if no revenue is generated, incorrect classification may impact financial disclosures or regulatory filings.
4. How often should non-commercial invoices be audited?
Quarterly internal reviews are recommended, with more frequent checks for high-volume operations.
5. Does automation completely eliminate compliance risk?
No system removes risk entirely, but automation significantly reduces human error and strengthens documentation controls.
6. What is the biggest compliance risk in non-commercial invoicing?
The most common risk is misclassification that leads to inaccurate revenue reporting or incomplete documentation.
7. How does centralized storage improve audit readiness?
Centralized systems allow instant access to historical records, ensuring transparency and faster response during regulatory reviews.
Conclusion
Automation plays a critical role in reducing compliance risks associated with non-commercial invoicing. By enforcing structured workflows, validating invoice data, and centralizing documentation, businesses improve non-commercial invoicing compliance while minimizing manual errors.
Structured invoice management protects financial integrity and ensures proper reporting. Without automation, misclassification and documentation gaps can create unnecessary exposure.
For organizations handling both revenue and non-revenue transactions, adopting automated systems provides clarity, control, and audit readiness. Strong governance today prevents costly compliance challenges tomorrow.

